Differenze tra le versioni di "Ampicillina"
| Riga 37: | Riga 37: | ||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| Riga 47: | Riga 53: | ||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| Riga 57: | Riga 69: | ||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| Riga 67: | Riga 85: | ||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| Riga 77: | Riga 101: | ||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| Riga 87: | Riga 117: | ||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
| + | |||
test | test | ||
Versione delle 22:36, 27 lug 2011
Indice
SPECIALITÀ
AMPICILLINA
- Ampicillina generico
- Ampilux COLL 3ML 0,8%
- Amplital 12CPS 500MG, 12CPR 1G, fiale 1G, fiale 500mg
AMPICILLINA/SULBACTAM
- Unasyn IM EV 500+250MG/1,6ML, IM 1FL 1G+500MG/3,2ML
STRUTTURA
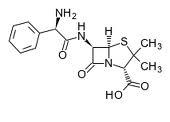
la struttura e' caratterizzata della presenza dell’anello beta-lattamico, legato ad un anello tiazolidinico
MECCANISMO D’AZIONE
E' un antibiotico beta-lattamico ad azione battericida tempo-dipendente. Agisce inibendo la sintesi della parete della cellula batterica .Infatti il peptidoglicano della parete cellulare batterica non essendo presente nelle cellule umane, rappresenta un bersaglio ideale per uccidere i batteri.
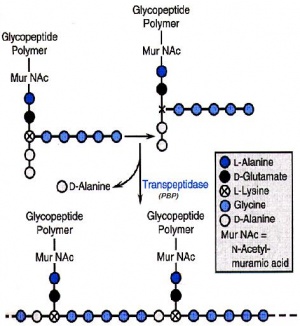
L'Ampicillina agisce al terzo stadio del processo di formazione del peptidoglicano , impedendo la formazione dei legami crociati della parete cellulare.
La formazione di tali legami è catalizzata da un gruppo di enzimi i PBP (penicillin binding proteins) localizzati sulla faccia esterna della membrana.
I PBP rimuovono un residuo di D-alanina terminale dal pentapeptide, rilasciando energia che viene utilizzata per la formazione dei legami crociati nel peptidoglicano.
L'Ampicillina inibisce le PBP mediante un meccanismo competitivo, perche somiglia al dimero D-ala D-ala.
Il legame betalattamico viene cosi scisso da parte dei PBP e l'Ampicillina scissa si fissa covalentemente all’enzima formando un complesso acil-enzima molto stabile.
Gli enzimi, così bloccati, non sono più in grado di catalizzare le reazioni di sintesi del peptidoglicano e il risultato finale e' una lisi della cellula batterica.
INDICAZIONI
test
test
test
test
test
test
test
CONTROINDICAZIONI
test
test
test
test
test
test
test
POSOLOGIA
test
test
test
test
test
test
test
AVVERTENZE
test
test
test
test
test
test
test
INTERAZIONI
test
test
test
test
test
test
test
EFFETTI COLLATERALI
test
test
test
test
test
test
test